
English Grammar is a vexing concept that comes into use at every turn in your digital life. It is here, you often encounter Grammar Nazis who would tear you limb to limb if you're found with a wrong grammar construct or a misspelled word.
You just cannot afford the time and energy to check every comment and every blabber by copying and pasting it into Microsoft word, just to check for mistakes. It simply seems too much work.
Introducing Grammarly, a service that can correct you anywhere, from typing in the hostile depths of social networks chained within 140 words, or replying to a racist comment at Facebook to mailing your boss about why you didn't submit the report.
We have with us Allison VanNest, Director of Public Relations at Grammarly. She seems petrifying, but trust me, Allie is a really bright and considerate professional who agreed to take time out of her busy schedule to let us trouble her with our questions.

Let me start with Grammarly first. It is a really efficient service that helps you write correct grammar in your everyday communications. The service works on several platforms and instantly points you towards an incorrect grammar construct or a misspelled word. You can then use it to provide correct alternatives to your incorrect sentence.
Grammarly is renowned worldwide as the best grammar checker there is. It was founded in 2009 by two entrepreneurs. Brad Hoover the CEO holds the reins of the san fransico based web service giant. The service can chekc more than 250 different types of grammatical errors that users often make. The website boasts more than 3 million users as of 2015 and has an alexa rank of less than 4000.
Grammarly has performed consistently well at its job and hence, won too many awards and accolades to even mention here. However in august 2013, Grammarly was ranked number 344 on Inc. magazine’s 32nd annual Inc. 500 list, an exclusive ranking of the nation’s fastest-growing private companies. It was also the finalist in the “Best Bootstrapped Startup” category in the 8th Annual Crunchies Awards in Feb 2015.
Introduction
Mohit: Tell us about the story of Grammarly, How did the idea take flight?
Allie: Grammar rules can be confusing, and they are constantly evolving. Grammarly was founded in 2008 by Alex Shevchenko and Max Lytvyn, both English language learners, to instantly and accurately provide written writing assistance to the more than two billion native and non-native English language speakers worldwide. The automated proofreading tool provides an easy way for students, professionals, job seekers, and English language learners to become more accurate English language writers.
About the Team
Mohit: Online service based companies are often depicted as geeky heaven with chocolate fountains, free food to sleeping pods. How is the work environment and culture at the offices of Grammarly?
Allie: At Grammarly, we codified our culture profile with one word -- EAGER. The goal is to have a memorable, understandable, and actionable company culture. While EAGER describes the attitude of Grammarly's team members, it’s also an acronym:
Ethical: Be honorable to earn trust. Do the right thing, even when no one is watching, without exception.
Adaptable: Embrace change, and learn in order to evolve and succeed. Apply a positive, problem-solving attitude.
Gritty: Demonstrate passion and perseverance for long-term goals, since persistence drives achievement. Do whatever it takes to get the job done, whenever it is necessary.
Empathetic: Treat others as you want to be treated, so we can work well together. Actively listen and put yourself in others’ shoes, and then respond accordingly.
Remarkable: Be recognized as exceptional yet humble, because talent drives impact. Seek out those who are exceptional and learn from them.
Although we have remarkable benefits at Grammarly – yoga, catered lunch, and more – we feel like the most important aspect of our work environment and culture is each other.
Tackling Competitors
Mohit: I'm sure you're aware that some websites have performed tests on Grammarly to check its accuracy. Some have found promising results (like me) but some (mostly rivals) have not. What is your opinion of such usage tests performed by individuals and rival firms on Grammarly?
Allie: We’re pleased you’ve found our product promising. The fact is that Grammarly’s ever-evolving algorithms work to accurately catch English spelling and grammar mistakes based on deviations from baseline grammar standards. For each potential issue flagged by Grammarly’s algorithms, users receive a detailed explanation so they can make an informed decision about how, and whether, to correct the mistake. While Grammarly’s algorithms are very powerful and constantly improving, they are not a replacement for a teacher or proofreader. Grammarly is an automated, cost-effective, and always-available tool to improve users’ English writing and skills.
On Social Networks
Mohit: You have a thriving Facebook community, which provides a platform for grammar discussions. With more than 4.5 million fans at facebook and nearing 2 million at Google plus, describe the challenges faced by your social media team in increasing and maintaining fans.
Allie: We actually don’t emphasize growing our social media fan base. It has been a fun thing for the team to watch, but it was never a sign of our success. Instead, Grammarly emphasizes engagement rates and reach. This has been the greatest challenge—to test, optimize, and adjust to make both our fans happy and the social algorithms. We’re just getting to know our audiences and responding. It’s just a conversation. Sometimes we say something wrong, but it informs how we say things moving forward.
On Business
Mohit: Cloud-based processing is often an advantage when you have exceedingly large algorithms to process the users' input. But this system often takes a hit in countries with no reliable internet connection. How do you propose to solve this?
Allie: Interestingly, some people who do have reliable access to the Internet are not able to make use of certain cloud-based tools for monetary reasons. That’s the first problem that the Grammarly team is tackling. Grammarly believes that quality writing improves confidence and credibility, and we know that everyone should have access to these personal and professional tools, regardless of income.
Through the launch of Grammarly’s Chrome extension, we’re now offering our quality spelling- and grammar-checking tool for free to users of Google Chrome. We hope to extend this functionality in 2015 to other browsers so that any writer with a reliable Internet connection can improve their credibility and communication style.
Mohit: Note. For those without Chrome, Grammarly services can be accessed from various portals including the Grammarly Plug-in for Microsoft Office Software or Grammarly Words, a contextual online thesaurus or the Grammarly Editor at Grammarly.com
Here we conclude this interview. Allie, I would like to thank you for taking time out of your schedule to help us understand the nitty-gritty of a service-based business and introducing us to Grammarly, which quite simply is an exceptional piece of work.
Our readers can pitch questions to Allie through the comment section and I'll make sure the questions reach Allie.
Related Reading
This was,







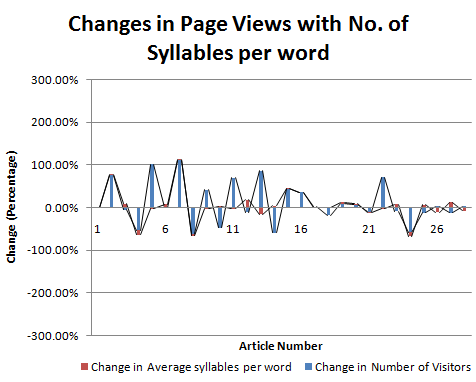







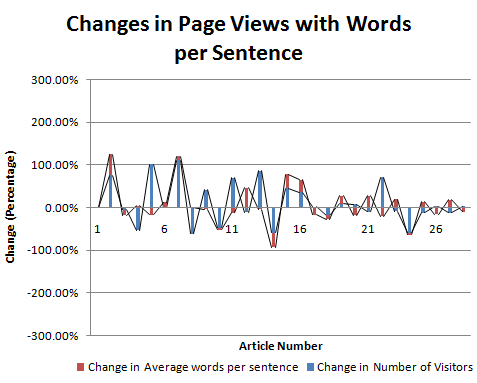















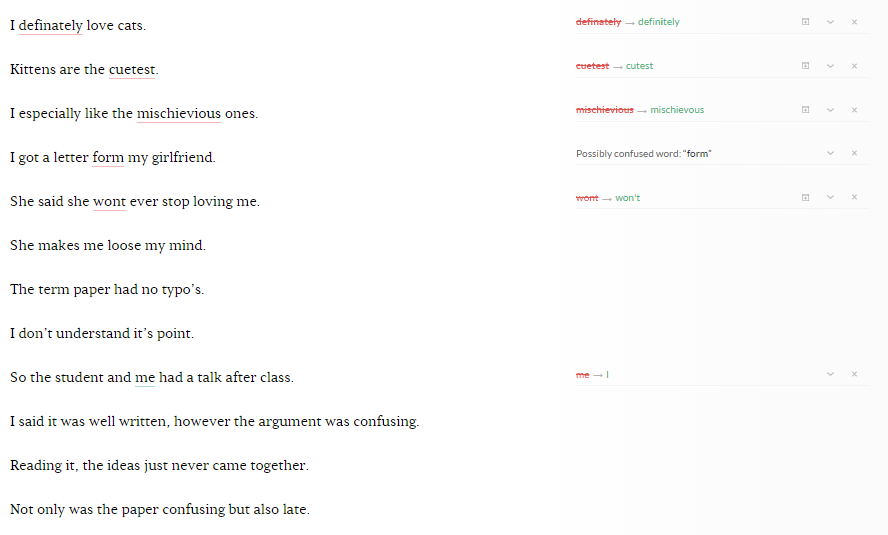















.png)

.png)